Umweltmodellierung
Umweltmodellierung
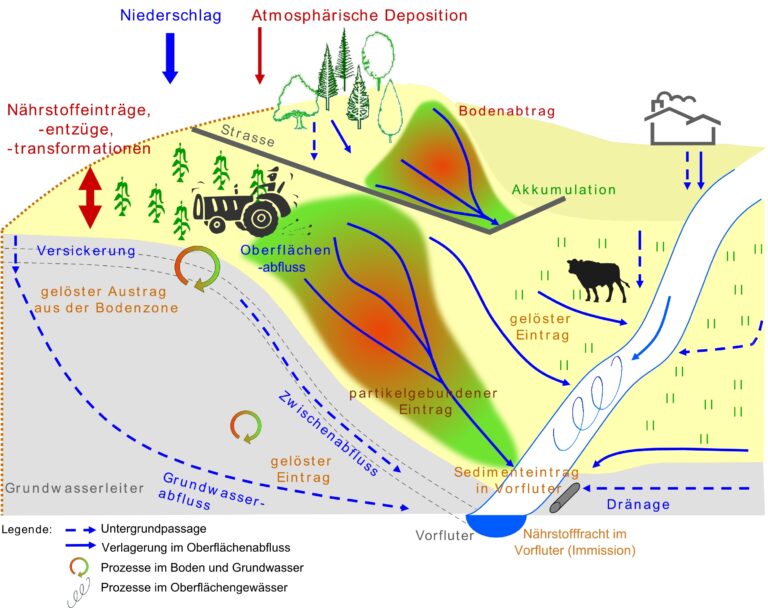
Modellsystem STOFFBILANZ
Das Modellsystem STOFFBILANZ (www.stoffbilanz.de) ist ein geowissenschaftliches Werkzeug zur Modellierung der Wasser- und Stoffflüsse in Einzugsgebieten, das wir fortlaufend weiterentwickeln. Es ermöglicht die Berechnung von Ist-Zuständen sowie Bewirtschaftungsszenarien und leitet Minderungsoptionen und -strategien für den Stoffeintrag in Grundwasser und Oberflächengewässer ab. STOFFBILANZ ist speziell für die Mesoskala entwickelt und stellt eine Verbindung zwischen groß- und kleinmaßstäbigen Verfahren her. Eine ausführliche Beschreibung des Modells finden Sie hier.
- Wasserhaushalt
- Stickstoff
- Phosphor
- Bewirtschaftungsszenarien
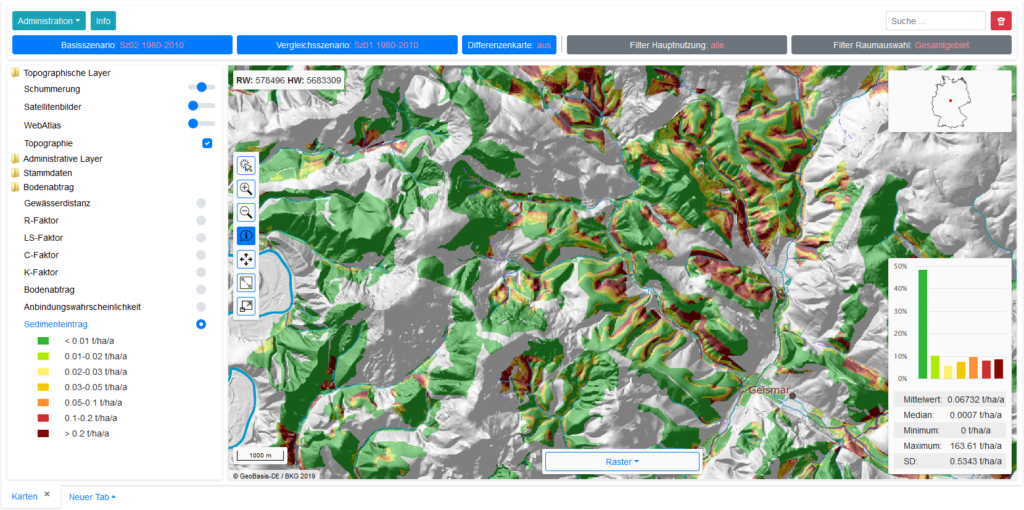
STOFFBILANZ Viewer
Um Nutzerfreundlichkeit, fachliche Aspekte und Anforderungen an das Flussgebietsmanagement miteinander zu verknüpfen, entwickelt VisDat den WebGIS-basierten STOFFBILANZ-Viewer. Dieser wird seit 2005 in zahlreichen Landes- und Bundesämtern in Deutschland sowie von internationalen Projektpartnern eingesetzt. In der Praxis erfolgt die systematische Betrachtung von Modellgebieten durch die Verwendung mehrerer, miteinander gekoppelter Einzelmodelle (z.B. Klima-, Wasserhaushalts-, Grundwasser-, Vegetationsmodelle) sowie von Messwerten unterschiedlichster Parameter. Der Aufwand für die Auswertung und Bereitstellung dieser immer umfangreicheren Datenbestände wird dabei oft unterschätzt. Hier unterstützt der STOFFBILANZ-Viewer die Fachanwender. Eine Beispielanwendung ist unter viewer.stoffbilanz.de auch öffentlich zugänglich.
- Wasserhaushalt
- Stickstoff
- Phosphor
- Bewirtschaftungsszenarien
Methodenentwicklung und Forschung
Unter Nutzung unserer Datenbank-, GIS- und Programmierumgebungen und unserem fachlichen Know how bringen wir Methoden aus den Bereichen Umweltanalyse, -bewertung sowie Okosystemdienstleistungen in die Praxis.
- Regressionsanalytische Verfahren zur Simulation von Gebietsabflüssen
- Tagesbasierte Simulation von Wasserflüssen
- Simulation des Bodenwasserhaushaltes
- Verdunstungsberechnungen (u.a. FAO-ET0, FAO-ETc)
- Simulation von Grundwasserverweilzeiten (Darcy)
- Berechnung der Retention von Sedimenten und Nährstoffen in Oberflächengewässern
- Tages-und jahresbasierte Simulation von Bodenerosion durch Wasser (USLE, M-USLE)
- Simulation von Sedimenteinträgen in Oberflächengewässer
- Simulation gelöster und partikelgebundener Stoffeinträge in Sickerwasser, Grundwasser und Oberflächengewässer
- Simulation von Maßnahmenwirkungspotenzialen für gelöste und partikelgebundene Stoffeinträge
- GIS-gestützte Reliefanalyse
- Digitale Satellitenbildauswertung
- Erstellung digitaler Bodenkarten und Bodeninformationssysteme
- Anwendung multivariater geostatistischer Verfahren
